NOTE: Many businesses only use their CRM after the initial meeting with a prospect. The smart move is to go the other way and leverage your CRM to record the activity of potential customers on social media prior to that first interaction. This can provide insights on their needs, plans, and expectations.
How to Successfully Implement CRM
Written by: Victoria Yu
Victoria Yu is a Business Writer with expertise in Business Organization, Marketing, and Sales, holding a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration from the University of California, Irvine’s Paul Merage School of Business.
Edited by: Sallie Middlebrook
Sallie, holding a Ph.D. from Walden University, is an experienced writing coach and editor with a background in marketing. She has served roles in corporate communications and taught at institutions like the University of Florida.
Updated on November 28, 2025

Taking good care of customers is always good for business – that’s why customer relationship management (CRM) is a $69 billion industry embraced by three out of four US sales teams. Studies show that implementing a quality CRM system can boost customer satisfaction and lead to a three-fold increase in sales.
But setting up a customer relationship management system is easier said than done, as there are a number of hurdles to clear before your business can leverage the benefits of CRM. Successful implementation requires careful planning, execution, and maintenance, and this step-by-step guide explains how to do it right.
Step 1: Define Your Goals and Objectives
Before you install a CRM system, it’s important to define your goals and objectives, which will depend on the needs of your business. What do you hope to achieve with the system? How do you expect to use it?
Common goals include:
- Increased Customer Retention – When you understand customer needs, you can provide personalized service, boosting satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improved Sales Performance – CRM systems help identify new sales opportunities and streamline sales processes, giving sales teams the info they need to close deals.
- Enhanced Marketing Effectiveness – CRMs analyze customer data and provide insights into behavior and preferences, enabling more targeted and effective marketing.
- Better Collaboration Across Departments – CRMs can facilitate better communication and collaboration across departments, increasing efficiency.
- Increased Productivity – Automating manual processes and providing easy access to data can reduce errors, improve response times, and increase productivity.
- More Accurate Forecasting and Reporting – CRMs provide real-time insights into customer behavior and performance, ensuring accurate forecasts and reports.
By defining your goals and objectives at the start, you set the stage for your CRM to meet your specific needs. At the end of the day, you don’t want to centralize customer data for the sake of centralizing customer data– you want your business to grow!
Step 2: Research and Choose the Best CRM System for Your Needs
There are many different CRM systems on the market, and you want to choose the one that fits your business. Top options include Zoho CRM, Salesforce Einstein, and HubSpot CRM.
Factors to consider
When making your choice, there are a number of factors to consider, such as:
- Features and Functionality – What features does the CRM offer? Do they meet your needs?
- Integration Capabilities – Can the CRM integrate with your existing systems and tools?
- Ease of Use – Is the CRM user-friendly? Will your team be able to use it effectively?
- Cost – This is a big one! What is the total cost of the CRM, including licensing, implementation, and maintenance?
CRMs aren’t interchangeable, so it’s important to educate yourself on what each one can and can’t do. Once you weigh their features against your goals and objectives, you’ll be fully informed to make the right choice.
Types of CRM
You have three types of CRM systems to choose from: collaborative, analytical, and operational. Be sure to choose the one that helps you achieve your goals.
| Collaborative | Analytical | Operational |
|---|---|---|
| Facilitates collaboration and communication between different teams or departments to improve customer service and support | Focuses on analyzing customer data to gain insights and improve decision-making | Focuses on automating and improving customer interactions, including sales, marketing, and customer service |
1. Collaborative CRMs
Collaborative CRMs include features for managing customer interactions and enabling teams to work together more effectively. This is done by sharing information, tracking customer interactions, and collaborating on tasks and projects.
CRMs can provide a more seamless and personalized customer experience. Sharing customer data helps meet customers’ needs in a timely and efficient manner. Collaboration, in general, helps ensure customers receive consistent, high-quality service across all channels.
A collaborative CRM usually includes several key features:
- Shared Customer Database – A shared customer database provides a central repository for your customer data. This ensures everyone has a real-time view of your customers and can provide personalized service.
- Collaboration Tools – Collaboration tools such as shared calendars, task lists, and messaging platforms aid team collaboration and communication.
- Multiple Channels of Customer Communication – Multiple channels of customer communication allow customers to interact with your business through their preferred method, whether it’s email, phone, message, or chat.
- Automated Workflows – Automated workflows for common tasks such as lead management, opportunity tracking, and customer support streamline processes and free up time for teams to focus on more strategic activities.
- Customer Analytics – Analytics tools provide insights into customer behavior. By incorporating customer preferences, you can provide more personalized service. You can also tailor marketing and sales efforts to the needs of your individual customers.
A collaborative CRM can provide a vast and detailed overview of your customer relations, helping teams craft more informed strategies. The result? Hopefully a better customer experience and more sales for your business.
2. Analytical CRMs
Analytical CRM systems use data mining and statistical analysis to identify trends in customer behavior and preferences, which is then used to shape marketing, sales, and service.
An analytical CRM collects data from transactions, website activity, social media, surveys and more. This data is then analyzed to generate reports and graphics. Key features of an analytical CRM system include:
- Data Warehousing – Store and manage large amounts of data from multiple sources
- Data Mining – Algorithms break down the data and identify patterns and trends
- Predictive Modeling – Helps forecast future customer behavior based on historical data
- Reporting and Visualization – Present insights in a way that’s easy to understand
Analytical CRM systems can help you make data-driven decisions based on a deeper understanding of your customers. You can improve customer satisfaction by addressing customers’ needs and preferences, boosting retention, and driving business growth.
3. Operational CRMs
Operational CRMs streamline processes, improve efficiency, and enhance the overall customer experience. Their key features include:
- Sales Force Automation – Automate lead prospecting by finding and prioritizing future customers
- Marketing Automation – Automatically creates, sends, and tracks emails and social media posts
- Customer Service and Support – Manages customer interactions and support requests, such as a ticketing system and a knowledge base
- Contact Management – Provides a centralized database of customer information, including contact details, purchase history, and preferences
These features aim to improve customer interactions and make managing customer relationships more efficient.
With so many CRM options, it’s a good idea to create a side-by-side comparison chart of the prices, features, and infrastructure requirements. Be sure to include compatibility, the type of setup, and any technical help you’ll need. This should give you a clear view of which CRM solution is the best fit for your business.
Step 3: Build and Train Your CRM Team
Implementing a CRM system requires cooperation from management, IT, sales, marketing, and customer service. It’s wise to involve all players from the start to ensure everyone is invested and understands the objectives.
To create an excellent CRM team, you’ll want to:
- Define your CRM strategy – Do you have a clear CRM strategy? It should detail your goals, target audience, and relevant business processes, and will serve as a sort of road map. Without it, your team building is likely to be directionless and uncertain.
- Identify key roles and responsibilities – Based on your road map, identify the key roles and responsibilities for implementing and maintaining your CRM, such as CRM manager, department champion, systems developer, data analyst, and QA engineer.
- Recruit team members – Now that you know what you need, find and recruit professionals with the relevant skills and experience. You may need to make some new hires, or you might be able to build out your team through internal recruiting.
- Provide training and support – Your team needs to be familiar with the CRM, its tools and features, as well as their responsibilities. This may include training materials, on-the-job training, and ongoing support and coaching.
- Foster collaboration and communication – Organize regular team meetings and status updates to encourage cooperation, collaboration, and solid communication. If the CRM team doesn’t get along, installation could be difficult.
- Measure and evaluate performance – The proof is in the pudding! In addition to your main goals, track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer satisfaction, sales revenue, and customer retention to gauge team performance and make decisions.
Step 4: Budget Your Costs and Benefits
Now it’s time for the fun part – running the numbers!
Costs
It’s a good idea to have your team forecast the financial impact of the CRM on your business before, during, and after implementation. Cost-benefit analyses and implementation timelines can provide real insight into expected return on investment, risks and challenges, and the duration of your install.
The cost of implementing a CRM system varies widely depending on the size of your business, your objectives, the number of users, the level of customization, and whether you’re deploying on-premise or using a cloud-based model.
Total costs tend to range from a few thousand dollars for a small business to a few million dollars for a vast corporation with complex needs.
Key costs associated with CRM implementation include:
- Software licensing fees
- Integration and customization costs
- Training costs
Keep in mind that production may decrease during rollout, as your resources are concentrated and your employees learn new skills.
Benefits
Guided by your objectives, come up with simple metrics to track and set clear targets to establish expectations. Measurable improvements in key areas like customer retention and conversion rates are likely to win over the CRM doubters.
Along the way, be sure to maintain an open channel for feedback from your team. They’ll be the first to see problems on the horizon and anticipate issues. The more comfortable your team members are passing info up the chain, the better it is for CRM implementation.
Step 5: Customize the CRM to Your Needs
Your business is unique, so it’s wise to customize your CRM to meet your needs. This may include customizing fields, workflows, and reports to match your business processes.
Customizing a CRM system involves configuring the system settings and functionality to align with your business. Here are some common steps involved in customizing a CRM system:
- Identify your business requirements – Before you start customizing, it’s important to have a clear understanding of your business requirements and how the CRM system can support them.
- Define your data model – Which types of data will your CRM store and examine? This is detailed in your data model, along with the relationships between different types of data. This is an important step in customizing the CRM system, as it will determine how you organize and access your data.
- Configure system settings – Most CRM systems allow you to configure a wide range of settings, such as user permissions, data fields, and email templates. This helps tailor the CRM system to your needs.
- Customize workflows – Workflows are automated processes that guide users through a specific task or activity. You can tell your CRM just how you like to do a wide variety of workflows, streamlining operations and automating routine tasks.
- Create custom reports and dashboards – Reporting and analytics are critical components of a CRM, allowing you to track KPIs and gain insights into your customer relations. With custom reports you can focus on the most important data.
- Integrate with other systems – If you use other software applications in your business operations, you may need to integrate them with your CRM.
It’s a good idea to have a deep understanding of your needs before customizing your CRM. Successful CRM debuts tend to occur when a business has invested the time and resources to appropriately configure the system.
Step 6: Migrate, Integrate, and Sync Data
We’re getting closer to the finish line. The next step is to determine which bits of data you want to migrate to your new CRM, and which data can be tossed out.
Migrate and Integrate
This process can take weeks, or even months, even if your data is neat and up-to-date. It’s important to collect and fix missing or incorrect data, otherwise it can reduce the effectiveness of the CRM. Too much data, especially at launch, can make it difficult for users.
Sync
When syncing, keep in mind that most CRMs have built-in programs that are similar to popular applications, such as calendar and notes apps. This makes syncing easy, as appointments and notes are automatically moved over and tracked.
But don’t forget to sync your CRM with external applications.
Step 7: Launch!
It’s go time! You’ve done all you can to ensure a successful launch and it’s time to flip the switch. Make sure the team is fully ready and all those who will use the CRM know when it’s coming online and when the old tools will be discontinued.
An implementation schedule with milestones for training completion, migration, and launch can boost morale and get everything off to a good start. You might also do a soft launch, for just a handful of key people, to test your CRM before the full launch.
Step 8: Monitor and Measure Performance
Implementing a CRM system is not a one-time event, but rather requires ongoing maintenance and monitoring. This is to gauge whether it’s meeting your objectives, and simply to make sure it’s performing as it should, and not malfunctioning in any way.
Take the time to regularly review your KPIs and analyze the data, allowing yourself to celebrate wins while identifying areas for growth.
Take a look at the most common challenges companies face when implementing CRM.
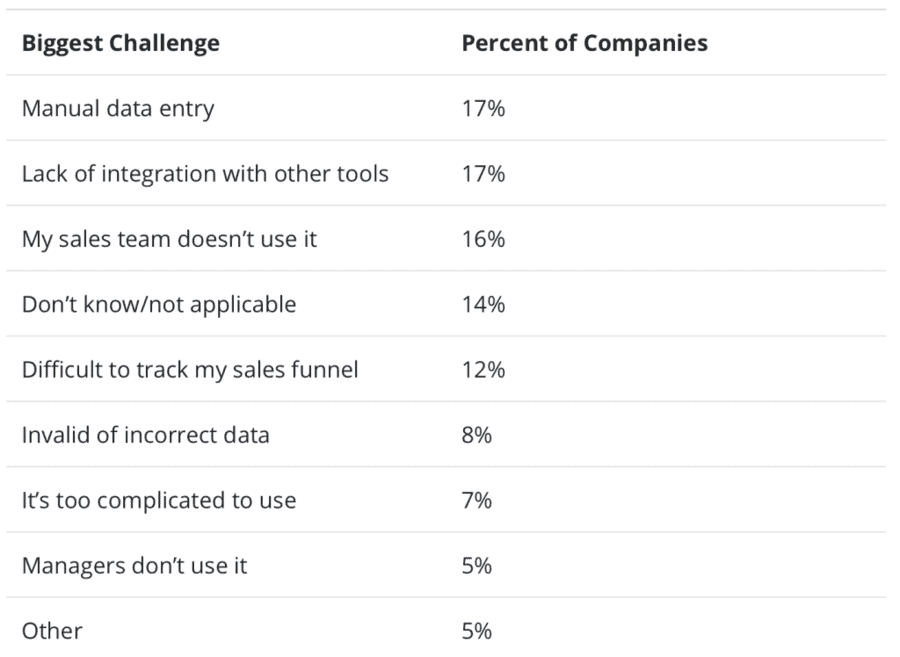
When facing a major issue, such as having a team that refuses to use the CRM, it’s tempting to swoop in and make vast personnel changes. But this often ends up eroding productivity, so it’s best to be patient with your CRM, allowing it to take root on its own time and introducing changes gradually.
At the same time, recognizing what’s not working can be as beneficial as acknowledging what is. Keep an eye out for weaknesses and shortcomings in your CRM and work to improve them.
Conclusion
Implementing a CRM system is an involved and complex process. Even so, it’s often worth it, as a quality CRM can have a massive impact on customer relations, sales, efficiency, and more.
Getting it done will require time, effort, and maybe a few trips back to the drawing board. But if you’re willing to develop the right strategy, you may find that implementing the right CRM has the potential to perfect your relationships with the people who drive your business.
FAQs
What are the benefits of implementing a CRM system?
Implementing a CRM system can help you improve customer satisfaction, increase sales, automate processes, reduce costs, and gain insights into customer behavior and preferences. The ultimate goal of a CRM is putting more money in your pocket by improving your relationship with your customers!
What are the key steps to implementing a CRM system?
The key steps to implementing a CRM system include defining business goals, selecting CRM software, customizing the software to meet specific needs, integrating with existing systems, training employees, and continually monitoring and optimizing performance.
How do I customize the CRM software to my business needs?
Most CRM software allows for customization through the use of templates, fields, workflows, and automation rules. Identify the specific needs of your business and work with the CRM provider to ensure that the software is tailored to meet those needs.
How do I integrate the CRM system with existing systems?
Integration with existing systems can be achieved through APIs, plugins, and third-party connectors. Work with the CRM provider and any other vendors to ensure that data can be seamlessly exchanged between systems.
How do I monitor and optimize the performance of the CRM system?
Regularly review key metrics such as customer satisfaction, sales, and engagement to identify areas for improvement. Continually test and optimize processes, workflows, and automation rules to ensure that the CRM system is meeting your business goals.
